Explain the Difference Between Random Sampling and Random Assignment.
Random Selection. The difference between these types of samples has to do with the other part of the definition of a simple random sample.
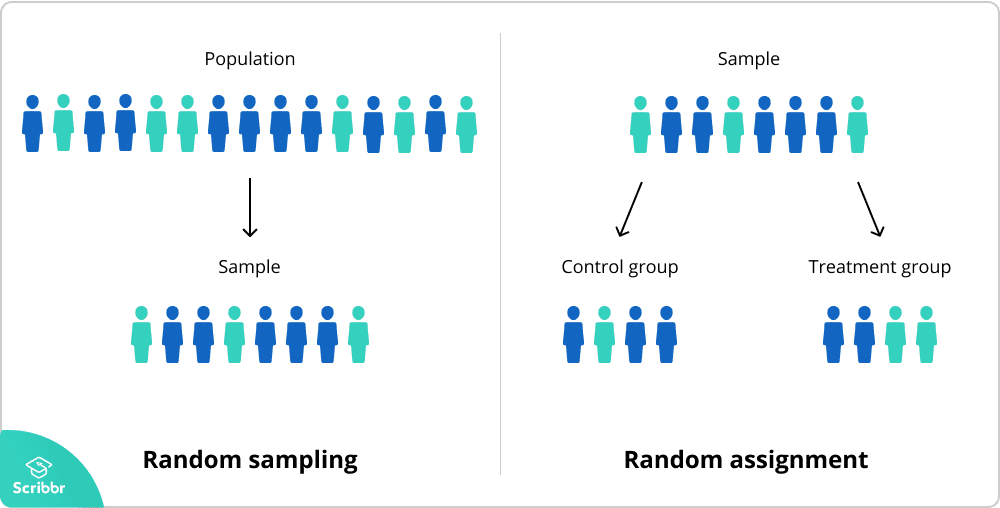
Random Assignment In Experiments An Easy Introduction
Random sampling is getting a sample to represent a population while random assignment uses a chance system to assign different subjects to experimental groups.

. Conduct both random sampling and random assignment. And then were gonna talk about the inferences that can made a CE a result of their brains Now plays what random assignment it was. Random assignment allows for inferences about cause and effect to be made as it limits variability.
More specifically it initially requires a sampling frame a list or database of all members of a populationYou can then randomly generate a number for each. There are 4 types of random sampling techniques. To ensure that members of each group in experiment is the same.
Why random sampling and assignment. Thus we have that random sampling allows for inferences about the population to be made since it is representative of the whole group. Random assignment allows us to make sure that the only difference between the various treatment groups is what we are studying.
Random Selection and Random Assignment. Random assignment refers to the process of randomly assigning the individuals in a study to either a treatment group or a control group. Part 1 Students compare distribution of random samples to population Observe that when many samples are taken sample means are.
Simple random can be used to cover the overall data population and selects. Explain the difference between random sampling and random assignment and indicate how these procedures affect a studys internal and external validity. And then were gonna talk about the inferences that can made a CE a result of their brains Now plays what random assignment it was.
Random sampling is a sampling technique where each sample has an equal probability of getting selected Non-random sampling is a sampling technique where the sample selected will be based on factors such as convenience judgement and experience of. Random assignment refers to how you place those participants into groups such as experimental vs. Question about asked us to consider the difference between random sampling and reigned in the Simon.
Random Sampling Techniques. Random selection refers to the process of randomly selecting individuals from a population to be involved in a study. Random assignment allows for inferences about cause and effect to be made as it limits variability.
Has to explain to the mayor the difference between random sampling and random assignment. The method by which those participants are divided into groups is referred to as random assignment. Random sampling also called probability sampling or random selection is a way of selecting members of a population to be included in your study.
For example if the total population is 51 female and 49 male then the sample should reflect those same percentages. In contrast random assignment is a way of sorting the sample participants into control and experimental groups. To be a simple random sample of size n every group of size n must be equally likely of being formed.
Random selection randomly selecting a group of people from a population the researcher selects a sample from a population using one of the random sampling techniques discussed earlier. The method of selecting individuals in a population to take part in your study is referred to as random sampling. A random sampling is the initial part of study deciding what you decide who is going to be included in this.
Random selection and random assignment are different and the difference must be understood. Random selection refers to how sample members study participants are selected from the population for inclusion in the study. As adjectives the difference between random and arbitrary is that random is having unpredictable outcomes and in the ideal case.
Simple random sampling requires using randomly generated numbers to choose a sample. A random sampling is the initial part of study deciding what you decide who is going to be included in this. Differences between random and stratified sampling.
Arbitrary is a synonym of random. A significant difference between samples not obtained using random sampling based on random assignment -- the cause of the difference between population means is the IV rather than a confound-causal links are important for forming and testing theories. Explain the difference between random sampling and random assignment and indicate how these procedures affect a studys internal and external validity.
Therefore results of the study can be generalized to the population. In order to generalize the results of an experiment to a larger group it is important to choose a sample that is representative of the qualities found in that population. Random selection or random sampling is a way of selecting members of a population for your studys sample.
Random assignment is an aspect of experimental design in which study participants are assigned to the treatment or control group using a. A systematic random sample relies on some sort of ordering to choose sample members. In contextmathematicslangen terms the difference between random and arbitrary is that random is mathematics of or relating to probability distribution while arbitrary is mathematics any and all possible.
You can think of random selection as the process you use to get the individuals in a study and you can think of. Random sampling allows for inferences about the population to be made since it is representative of the whole group. 644 Explain the difference between random sampling and random assignment.
Question about asked us to consider the difference between random sampling and reigned in the Simon. In contrast random assignment is a way of sorting the sample into control and experimental groups. So to summarize random sampling refers to how you select individuals from the population to participate in your study.
Random sampling allows us to obtain a sample representative of the population. Random sampling refers to randomly drawing sample from the population for the sample while random assignment refers to assigning people randomly to control and experiment groups View the full answer. Random sampling gives every individual an.
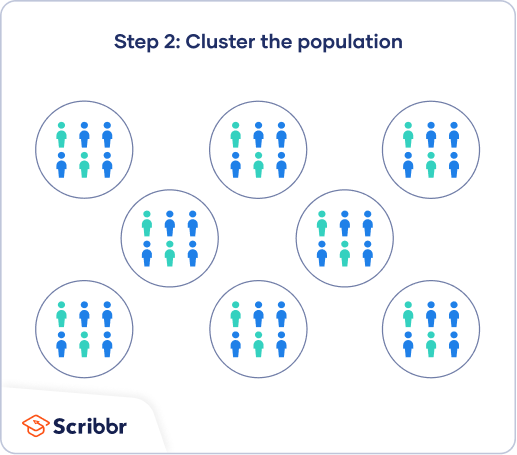
Cluster Sampling A Simple Step By Step Guide With Examples

Statistics Random Vs Simple Random Sample Youtube

Stratified Random Sampling A Method Of Probability Sampling Probability Research Phd
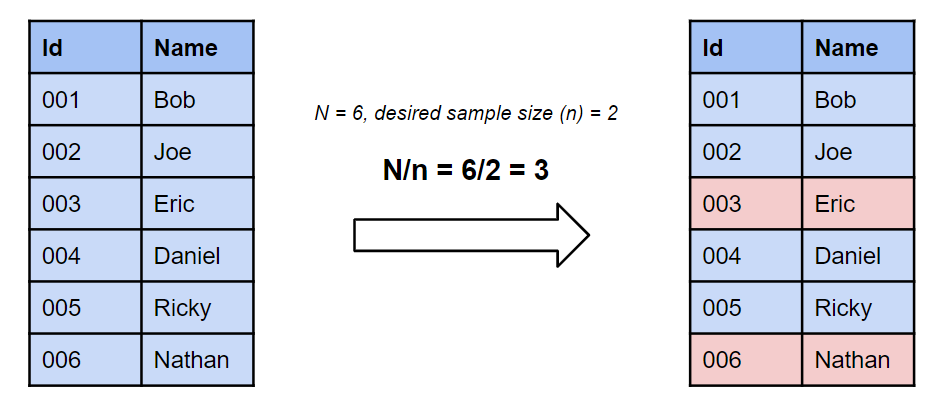
Four Types Of Random Sampling Techniques Explained With Visuals By Terence Shin Towards Data Science
Systematic Random Samples Definition Formula Advantages Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Four Types Of Random Sampling Techniques Explained With Visuals By Terence Shin Towards Data Science

Four Types Of Random Sampling Techniques Explained With Visuals By Terence Shin Towards Data Science

Random Sample V Random Assignment Youtube
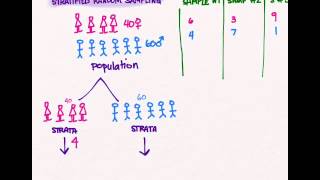
Sampling 03 Stratified Random Sampling Youtube
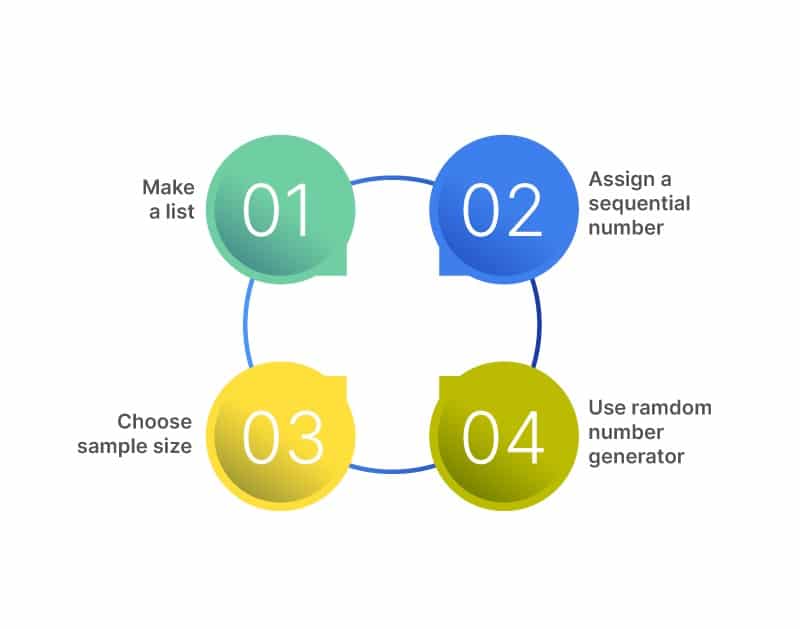
Simple Random Sampling Definition Method Examples
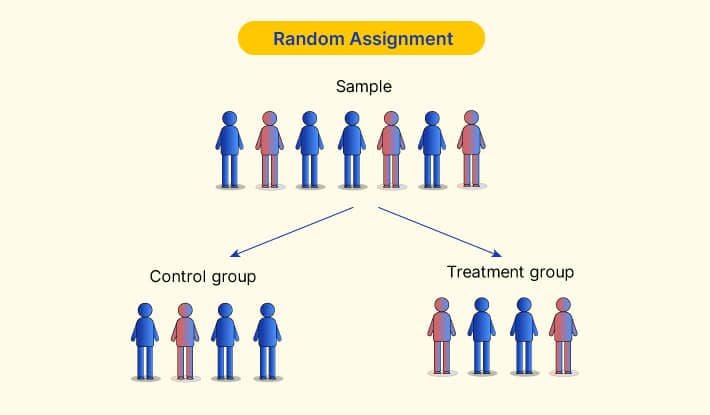
Introduction To Random Assignment Voxco

Four Types Of Random Sampling Techniques Explained With Visuals By Terence Shin Towards Data Science
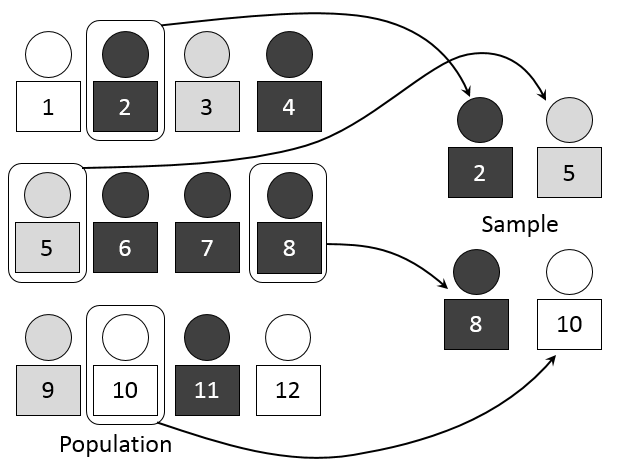
Randomization In Statistics And Experimental Design Statistics How To

Random Sampling Random Assignment Assignments Psychology Inference

There Are Two Types Of Non Probability Sampling Purposive Sampling And Probability Research Methods Observational Study
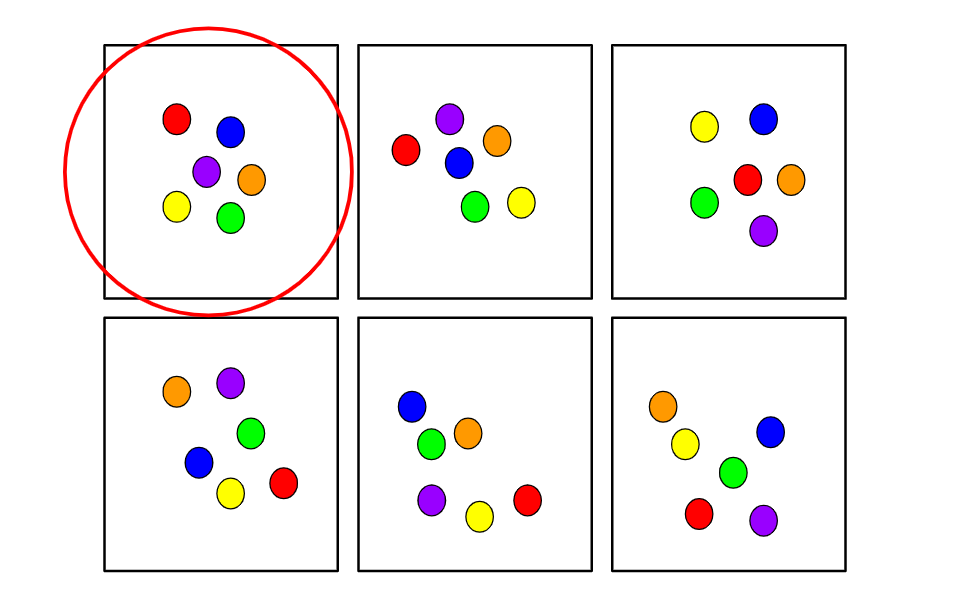
Four Types Of Random Sampling Techniques Explained With Visuals By Terence Shin Towards Data Science


Comments
Post a Comment